2 Getting to know about Deep Neural Network
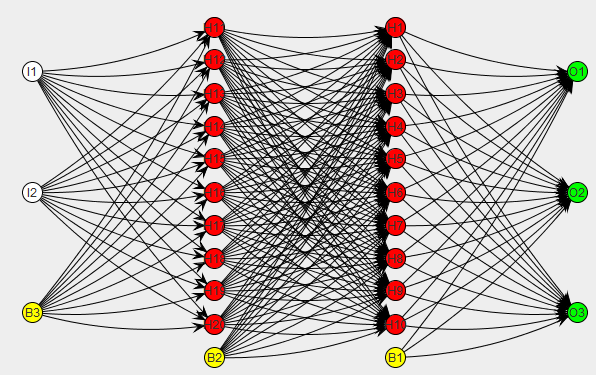
Image Source: https://machprinciple.wordpress.com/2013/11/09/neural-network-controlled-spacecraft-control-logic-exists/
2.1 Introduction
A Deep Neural Network (DNN) is an artificial neural network (ANN) with multiple hidden layers of units between the input and output layers. Similar to shallow ANNs, DNNs can model complex non-linear relationships. DNN architectures (e.g. for object detection and parsing) generate compositional models where the object is expressed as a layered composition of image primitives. The extra layers enable composition of features from lower layers, giving the potential of modeling complex data with fewer units than a similarly performing shallow network.
DNNs are typically designed as feedforward networks, but research has very successfully applied recurrent neural networks, especially LSTM, for applications such as language modeling. Convolutional deep neural networks (CNNs) are used in computer vision where their success is well- documented. CNNs also have been applied to acoustic modeling for automatic speech recognition, where they have shown success over previous models.
This tutorial will cover DNNs, however, we will introduce the concept of a “shallow” neural network as a starting point.
2.2 History
An interesting fact about neural networks is that the first artificial neural network was implemented in hardware, not software. In 1943, neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and mathematician Walter Pitts wrote a paper on how neurons might work. In order to describe how neurons in the brain might work, they modeled a simple neural network using electrical circuits. [1]
2.3 Backpropagation
Backpropagation, an abbreviation for “backward propagation of errors”, is a common method of training artificial neural networks used in conjunction with an optimization method such as gradient descent. The method calculates the gradient of a loss function with respect to all the weights in the network. The gradient is fed to the optimization method which in turn uses it to update the weights, in an attempt to minimize the loss function.
2.4 Architectures
2.4.1 Multilayer Perceptron (MLP)
A multilayer perceptron (MLP) is a feed- forward artificial neural network model that maps sets of input data onto a set of appropriate outputs. This is also called a fully-connected feed-forward ANN. An MLP consists of multiple layers of nodes in a directed graph, with each layer fully connected to the next one. Except for the input nodes, each node is a neuron (or processing element) with a nonlinear activation function. MLP utilizes a supervised learning technique called backpropagation for training the network. MLP is a modification of the standard linear perceptron and can distinguish data that are not linearly separable.
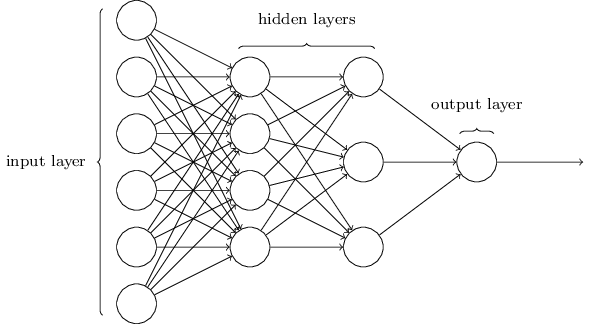 Image Souce: neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com
Image Souce: neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com
2.4.2 Recurrent
A recurrent neural network (RNN) is a class of artificial neural network where connections between units form a directed cycle. This creates an internal state of the network which allows it to exhibit dynamic temporal behavior. Unlike feed-forward neural networks, RNNs can use their internal memory to process arbitrary sequences of inputs. This makes them applicable to tasks such as unsegmented connected handwriting recognition or speech recognition.
There are a number of Twitter bots that are created using LSTMs. Some fun examples are [@DeepDrumpf](https://twitter.com/DeepDrumpf) and [@DeepLearnBern](https://twitter.com/DeepLearnBern) by Brad Hayes from MIT.
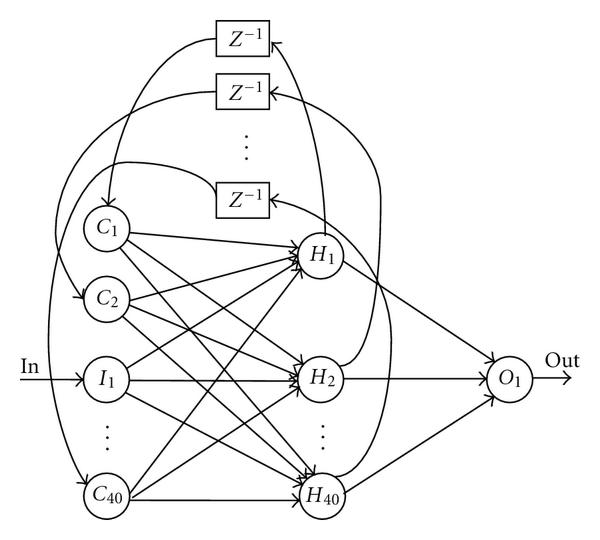
2.4.3 Convolutional
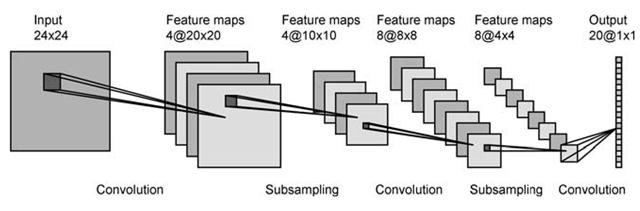
A convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a type of feed- forward artificial neural network in which the connectivity pattern between its neurons is inspired by the organization of the animal visual cortex, whose individual neurons are arranged in such a way that they respond to overlapping regions tiling the visual field. Convolutional networks were inspired by biological processes and are variations of multilayer perceptrons designed to use minimal amounts of preprocessing. They have wide applications in image and video recognition, recommender systems and natural language processing.
Some creative application of CNNs are DeepDream images and Neural Style Transfer.
2.5 Visualizing Neural Nets
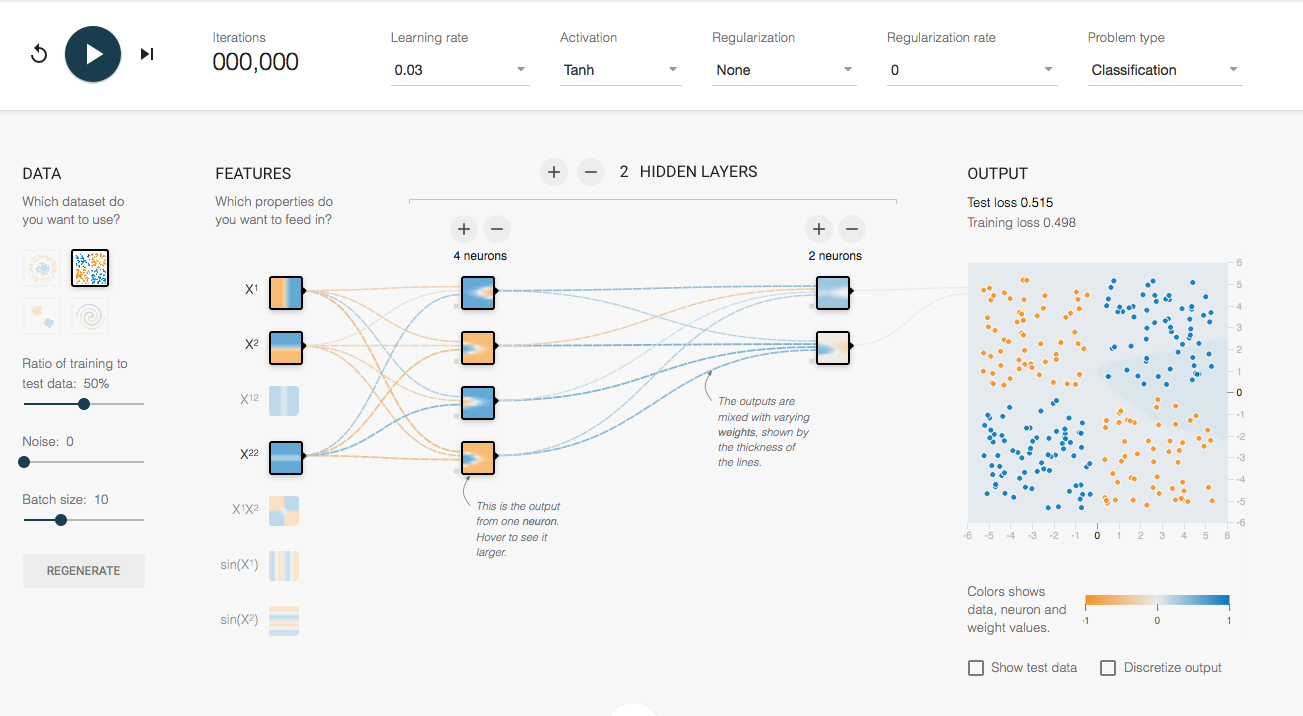
http://playground.tensorflow.org is a website where you can tweak and visualize neural networks.